- Investing
- >
- Basics
- >
- Financial Statements
- >
- Income Statement
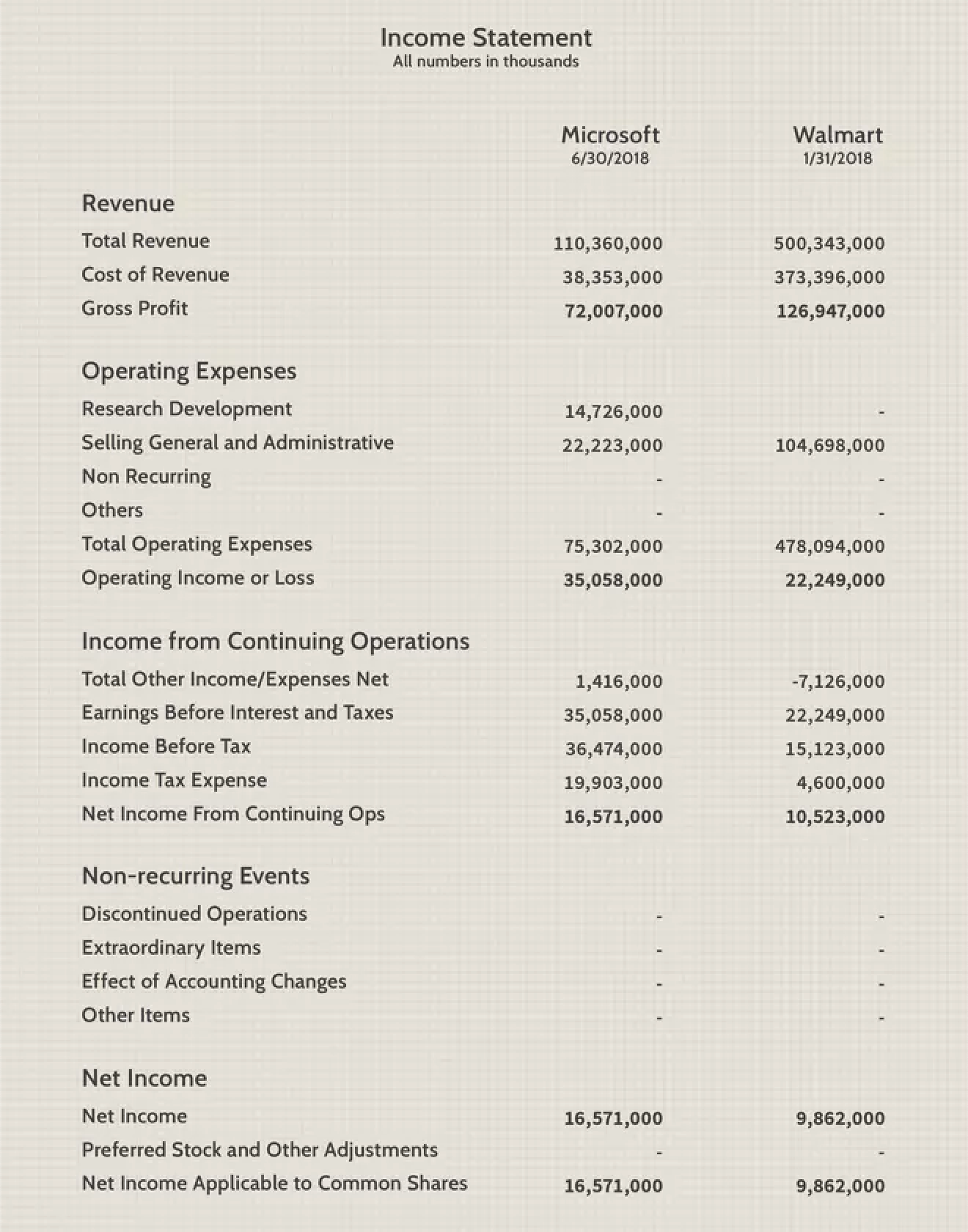
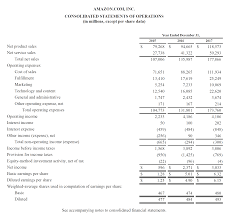
Income Statement
Also known as the profit and loss statement or the statement of revenue and expense, the income statement primarily focuses on the company's revenue and expenses during a particular period.
An income statement is one of the three (along with balance sheet and statement of cash flows) major financial statements that reports a company's financial performance over a specific accounting period.
Net Income = (Total Revenue + Gains) – (Total Expenses + Losses)
Total revenue is the sum of both operating and non-operating revenues while total expenses include those incurred by primary and secondary activities.
An income statement provides valuable insights into various aspects of a business. It includes a company’s operations, the efficiency of its management, the possible leaky areas that may be eroding profits, and whether the company is performing in line with industry peers
The income statement shows the performance of the business throughout each period, displaying sales revenue at the very top. The statement then deducts the cost of goods sold (COGS) to find gross profit. From there, the gross profit is affected by other operating expenses and income, depending on the nature of the business, to reach net income at the bottom – “the bottom line” for the business.
Key features:
- Shows the revenues and expenses of a business
- Expressed over a period of time (i.e., 1 year, 1 quarter, Year-to-Date, etc.)
- Uses accounting principles such as matching and accruals to represent figures (not presented on a cash basis)
- Used to assess profitability